Static Testing of DC Machines

Key Testing Methods for DC Motors
-
Field Frame Tests:
- Winding resistance, inductance, impedance.
- Insulation-to-earth tests (e.g., Megger tests).
- Surge tests for turn-to-turn insulation weakness.
-
Armature Tests:
- Includes winding resistance, commutator checks, and equalizer coil tests.
- Specialised tests: span testing and bar-to-bar surge testing.
Modern Testing Equipment and Techniques
-
Bar-to-Bar Testing:
- Detects faults like short circuits, weak insulation, and open circuits.
- Low-resistance measurements between adjacent bars using Kelvin methods.
- Modern devices produce reports and bar charts, eliminating manual error.
-
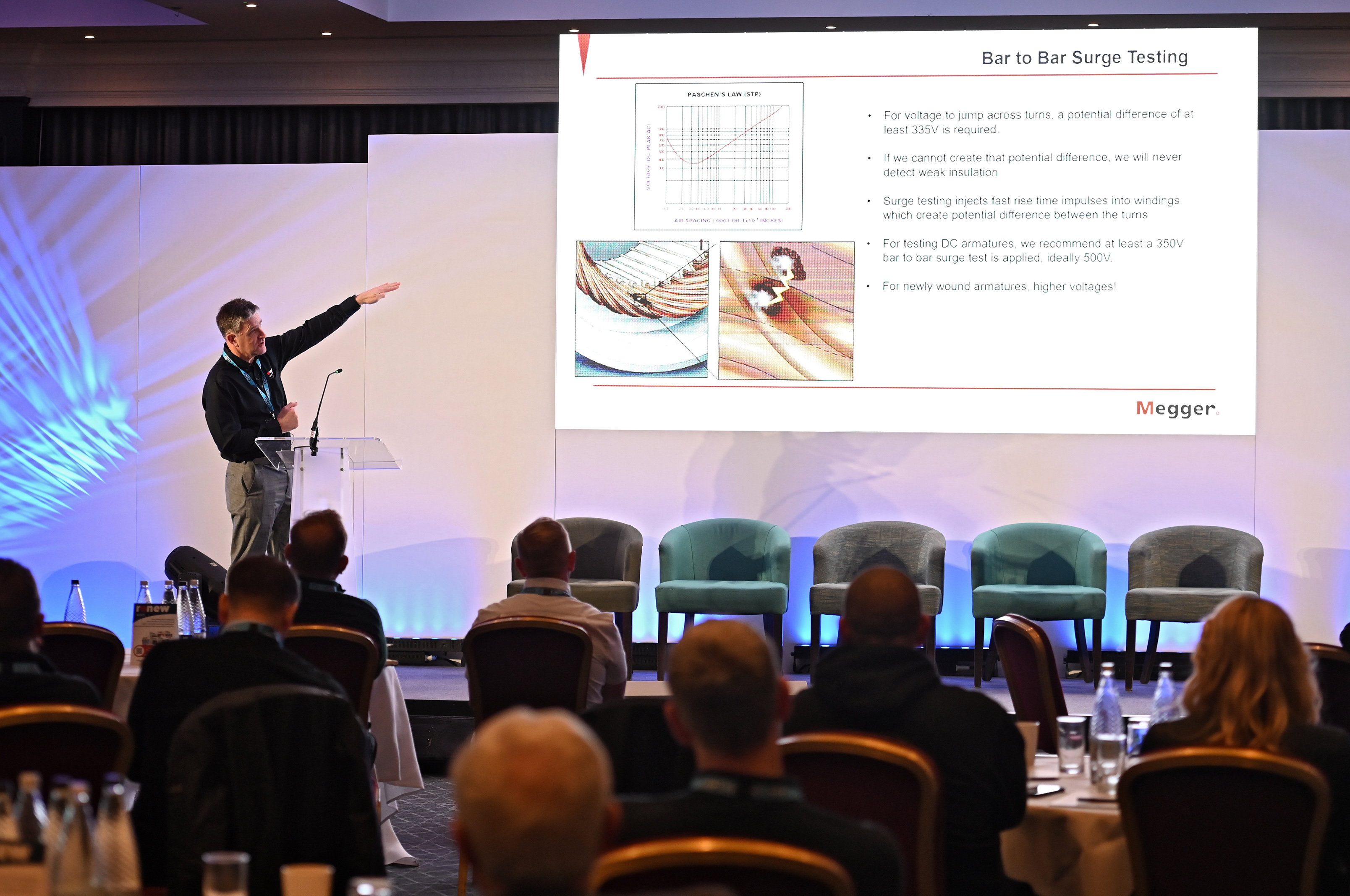
Surge Testing:
- Detects insulation weaknesses between turns using potential differences.
- Relies on Parian’s Law, which requires a voltage differential between conductors to identify faults.
- Demonstrated with two examples:
- No potential difference: insulation withstood 15kV without breakdown.
- With potential difference: insulation breakdown occurred below 8kV.
Advanced Techniques for Armatures
- Span Testing:
- Compares groups of bars.
- Effective for smaller armatures but less sensitive for large, low-impedance armatures.
- Bar-to-Bar Testing:
- Required for large armatures to create necessary potential differences.
- High-current surge testers ensure precision and reliability.
- Recorded data allows easy comparison and traceability for customers.
Modern Test Equipment Features
- Automated recording and reporting for speed and accuracy.
- Adjustable tolerances to flag deviations.
- High-current surge testers for large armatures.
- Traceable results enhance customer trust and ensure compliance.